A Colourless, Extremely Hazardous Liquid Known As Carbon Tetrachloride Has Been Employed Extensively In A Variety Of Industrial Applications
Carbon Tetrachloride is a colorless and volatile liquid that has a sweet odor. It is also known by its chemical formula, CCl4, and is a member of the halocarbon family of organic compounds. Carbon chloride was once widely used in industrial and commercial applications, but its use has declined due to its toxic nature and potential harm to the environment.
History of Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon chloride was first synthesized in 1839 by the French chemist Henri Victor Regnault. It was initially used as a solvent for oils and fats and as a refrigerant in cooling systems. Later, it was used as a fire extinguisher and a fumigant for stored grain and other crops.
The size of the worldwide Carbon Tetrachloride Market is anticipated to increase in the near future and develop at a CAGR of 4.9% over the projected period (2019 - 2027).
In the 20th century, carbon chloride was used extensively as a cleaning agent for electrical equipment and as a solvent for the dry cleaning industry. However, in the 1970s, concerns were raised about the harmful effects of carbon chloride on human health and the environment, and its use was subsequently phased out in many countries.
Properties and Structure of Carbon Tetrachloride
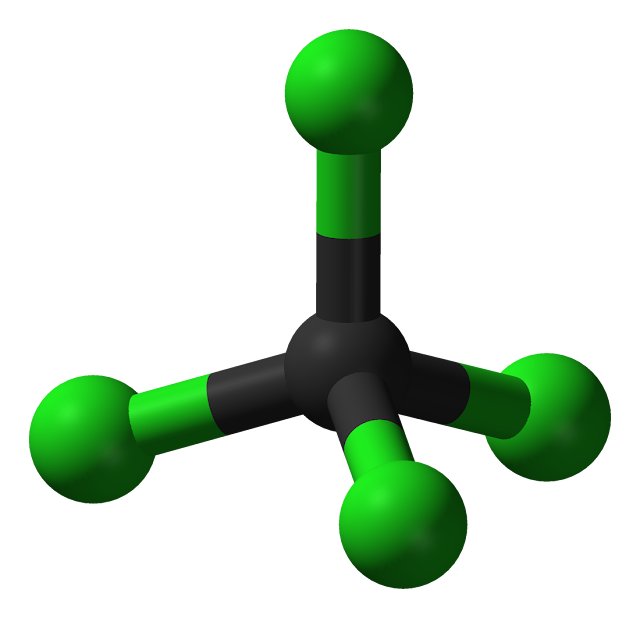
Carbon chloride is a nonpolar molecule, which means that it does not have a net dipole moment. It has a tetrahedral shape, with the carbon atom at the center and four chlorine atoms surrounding it. The carbon-chlorine bond in carbon chloride is polar, but the molecule as a whole is nonpolar due to the symmetric arrangement of the chlorine atoms.
Carbon Tetrachloride has a boiling point of 76.7°C and a melting point of -23°C. It is soluble in organic solvents such as benzene and chloroform but is insoluble in water.
Gcc Industrial Gases are essential for brazing, food processing, cutting, treating metals, refining, and welding.
Carbon chloride was widely used in the past as a solvent for oils and fats, a refrigerant, a fire extinguisher, and a fumigant for stored crops. It was also used in the production of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and as a cleaning agent for electrical equipment and in the dry cleaning industry.



Comments
Post a Comment