Transcatheter Heart Valve Should be Selected According to The Characteristics of The Patient or Should They be Uniformly Designed?
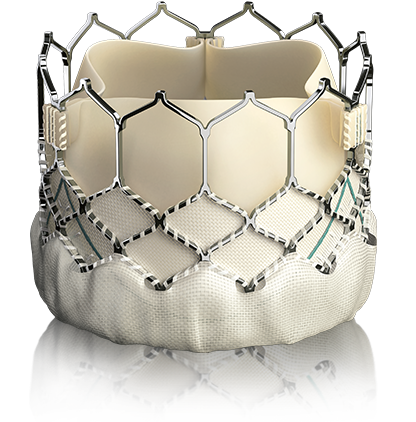 |
| Transcatheter Heart Valve |
Transcatheter Heart Valve replacement has become the standard procedure for aortic valve, mitral valve, and pulmonary valve replacement over the last decade. Transcatheter heart valve replacement is a minimally invasive method for treating severe aortic stenosis and mitral regurgitation by replacing the heart valve with a prosthetic valve. It is a viable alternative to invasive open heart surgery, particularly for high-risk patients.
As a result, the operation aids in the reduction of severe degenerative aortic stenosis and improves patient survival rates. The growing prevalence of severe aortic stenosis asymptomatic, severe aortic stenosis asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis asymptomatic severe aortic steno.
More than 7 million people worldwide die each year from sudden cardiac arrest. As a result, the Transcatheter Heart Valve Market replacement is aided by the rising number of heart attacks, heart failures, strokes, and other heart-related illnesses. Better treatment and greater accessibility to TAVR devices have emerged from technological developments and novel product releases in the cardiovascular business. Tissue valves are becoming more popular than mechanical prosthetic valves due to their superior biocompatibility and durability. Favorable reimbursement methods for Medicare, Medicaid, and insurance claims sponsored by regulatory authorities for patients increase the affordability of these transplant surgeries, boosting the valvular condition treatment rate.
TAVR is also utilised to treat aortic valve problems such as severe aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, and others, depending on the application. Transcatheter Heart Valve replacement devices combine a mechanical valve (made of stainless steel or nitinol) with biological valve leaflets (made of cow heart tissue or bovine). These aortic valves come in a variety of sizes (29mm, 22mm, 20mm, 18mm, 14mm, and 16mm). Transcatheter mitral valve replacement, on the other hand, improves hemodynamic efficiency by reducing residual mitral regurgitation and lowering transvalvular gradients. Mechanical valves and bioprosthetic tissue valves are two types of transcatheter mitral valve replacement.



Comments
Post a Comment